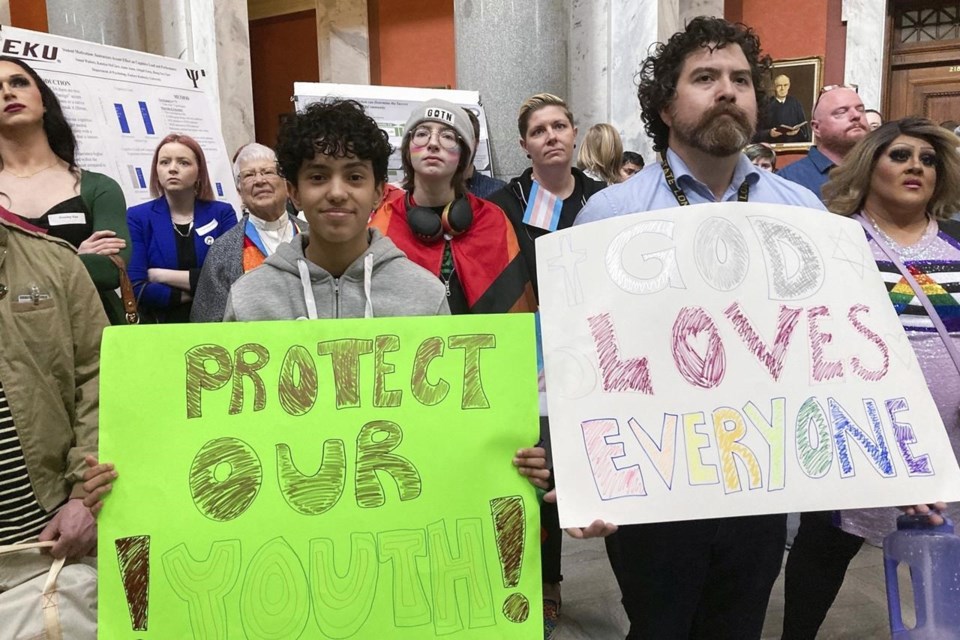FRANKFORT, Ky. (AP) — Kentucky Gov. Andy Beshear's veto of a bill aimed at transgender health care puts the state in the middle of a national fight, but with more immediate consequences as the state's looming election offers an early test on the state-by-state assault on gender-affirming care for minors.
The veto issued Friday set off competing messages likely to be repeated until the November election — when Bluegrass State voters will decide whether to reward the Democratic governor with a second term or hand over the governor's office to a Republican. No one seems to know yet how much weight voters will put on the transgender issue with the general election more than seven months away.
The legislation in Kentucky is part of a widespread movement, with Republican state lawmakers in other states approving extensive measures that restrict the rights of LGBTQ+ people this year, from bills targeting trans athletes and drag performers to measures limiting gender-affirming care.
Beshear framed the Republican-backed bill in Kentucky as an example of government overreach into parental rights. The sweeping bill would ban gender-affirming care for minors — one of many provisions that would affect the lives of young transgender people.
“At the end of the day, this is about my belief — and, I think, the belief of the majority of Kentuckians — that parents should get to make important medical decisions about their children, not big government," Beshear told reporters soon after his veto.
Kentucky's GOP-dominated legislature passed the bill by lopsided margins. Lawmakers will reconvene Wednesday for the final two days of this year’s session, when they could vote to override the veto.
Republicans took immediate aim at the governor's veto, saying he veered too far for most Kentuckians. Republican Party of Kentucky spokesperson Sean Southard asked: “Is Andy Beshear the governor of Kentucky or California?” He predicted the governor will pay a political price for his action.
"Once this campaign is over, today may very well be remembered as the day Andy Beshear lost his bid for reelection,” Southard said Friday.
Republicans could try to capitalize on the political divide over transgender rights to motivate socially conservative voters to flock to the polls in November, when state constitutional offices are on the ballot. Several leading GOP contenders for governor were aligned in condemning Beshear's veto.
“If the Republicans choose to make this a centerpiece of the campaign against Beshear, it’s going to hurt him,” said Scott Jennings, a Kentucky-based Republican political commentator.
Beshear cited his own religious faith as a factor in rejecting the bill, saying: “I believe every single child is a child of God.”
Twelve candidates in all are competing for the Republican nomination for governor in the state's May primary. Beshear’s bid for a second term is drawing national attention to see if the popular incumbent can win again in the Republican-trending state. Beshear has won praise for his responses to devastating tornadoes and flooding, as well as a series of economic development successes.
The bill's opponents say they've got the public on their side and predict Beshear will benefit. They pointed to statewide polling released last month showing a majority of Kentuckians believe decisions over a transgender teen’s health care should be left with the parent, not determined by the state.
“Folks who have never been involved with politics or legislation have been activated by the Kentucky General Assembly’s all-out war on LGBTQ kids,” said Chris Hartman, executive director of the Kentucky-based Fairness Campaign.
Social conservatives in Kentucky were dealt a setback in last year's general election when statewide voters rejected a ballot measure aimed at denying any constitutional protections for abortion.
The transgender health care bill sparked emotional responses from opponents as it was fast-tracked to legislative passage by GOP supermajorities in mid-March. It would ban gender-affirming care for transgender minors. It would outlaw gender reassignment surgery for anyone under 18, as well as the use of puberty blockers and hormones, and inpatient and outpatient gender-affirming hospital services.
Doctors would have to set a timeline to “detransition” children already taking puberty blockers or undergoing hormone therapy. They could continue offering care as they taper a child’s treatments if removing them from the treatment immediately could harm the child.
The bill’s supporters say they're trying to protect children from undertaking gender-affirming treatments they might regret as adults. Research shows such regret is rare. Gender-affirming medical treatments have long been available in the U.S. and are endorsed by major medical associations.
The bill would require school districts to devise bathroom policies that, “at a minimum,” would not allow transgender children to use the bathroom aligned with their gender identities. And it would allow teachers to refuse to refer to transgender students by the pronouns they use and would require schools to notify parents when lessons related to human sexuality are going to be taught.
Debates over transgender rights garnered considerable attention throughout Kentucky's legislative session, but in Pike County in eastern Kentucky, the issue has been a non-factor, said Pike County Judge-Executive Ray Jones II, a Democrat who supports Beshear.
“It’s not even been an issue up here," said Jones, a former state senator. "People are worried about inflation, they’re worried about the economy, they’re worried about jobs. Nobody’s called my office to discuss transgender issues.”
Summing up the potential political fallout from the veto, Jones said: “People who would vote because of the governor’s veto would likely not vote for him anyway.”
Bruce Schreiner, The Associated Press