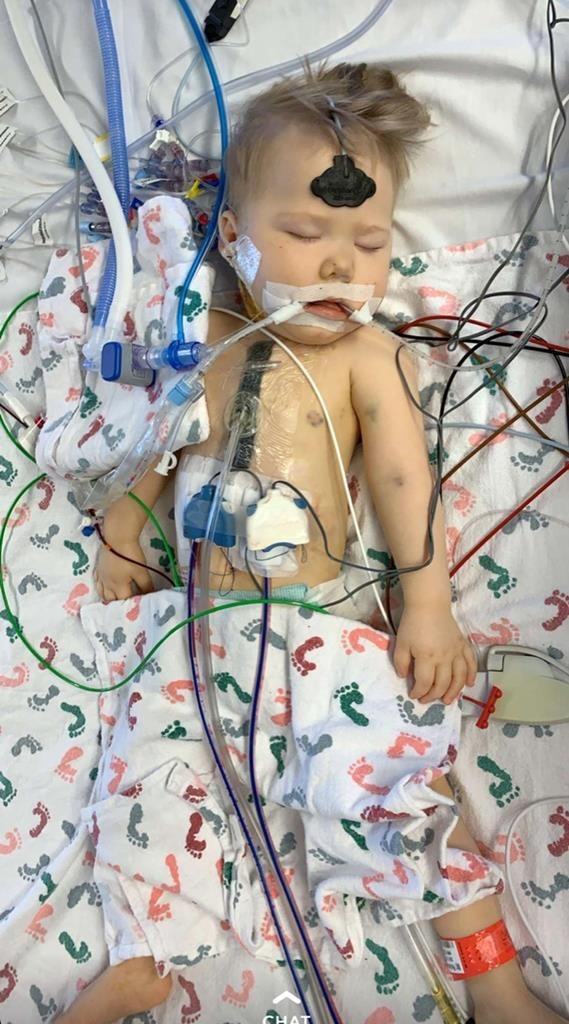
Greyson Parisien’s time on earth was short. But the boy with dark-rimmed eyeglasses who was enchanted by the music in “Frozen,” the sound of ripping paper and his dad playing the guitar is having an outsized impact on his tribal community in the far reaches of North Dakota.
His journey to correct an irregular heart led the Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians to add an organ donation box to tribal IDs, which it unveiled during a November ceremony.
The rate of organ donations among Native Americans is much lower than other ethnic groups. For some tribes, cultural beliefs are a factor. In rural communities, time, distance and spotty internet access can hinder the process.
“You don’t think about donation and how many people are not donors,” said Greyson’s grandmother, Joan Azure. “I was thinking, ‘There has to be more donors.’ When you’re going through this personally, you don’t want someone to die but you also want your child to live.”
Fewer than 1% of the 100,000 people nationwide waiting for organ transplants are Native Americans, who make up nearly 3% of the U.S. population.
The figures are higher in some states, including New Mexico where 1 in 5 people on the waiting list are Native American. In South Dakota, North Dakota and Minnesota, nearly 5% of patients awaiting an organ donation are Native American.
Greyson had surgery at 5 months to correct a heart problem, and then he needed an external device to pump blood through his small body. A heart transplant allowed him to leave the hospital after a year and return to the Turtle Mountain reservation, headquartered in Belcourt, North Dakota.
Tribal members followed Greyson's treatment through updates his family posted on social media. They saw him hooked up to medical equipment and dressed sharply in boxy eyeglasses, bow ties and khakis, his hair combed in a mohawk.
When he died suddenly of pneumonia in September 2019, the community sought understanding and assurance that it wasn't because of his new heart. He was 21 months old.
Greyson’s story and spirit live on in parades, powwows and conversations. Joan Azure also highlights her grandson during a week devoted to children born with congenital heart problems.
The Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians honored Greyson this year with a resolution to add an organ donation box to tribal IDs. The tribe unveiled the IDs in November, waived the $10 fee and encouraged tribal members to check the box.
“Today is a monumental day that people will remember, especially Native nations, for decades to come,” tribal Chairman Jamie Azure said, standing next to Greyson’s photo, was taken after he got a new heart — smiling with arms stretched to the sky.
The tribe believes it could be the first of the 574 federally recognized Native American nations to designate a spot on tribal IDs for organ donors.
Susan Mau Larson, the chief strategy officer for LifeSource, part of a network of nearly 60 organ procurement organizations, said she hopes other tribes follow suit. Several are working with tribal communities to raise awareness of organ donation and transplant.
Those conversations can be tough, especially when personal or traditional beliefs don’t align with Western medicine. They happen in tribal communities, at events and in hospital rooms as someone nears the end of their life. And there are guidelines: Identify the decision maker in a family. Tell a story, don’t explain the process. Give the family time to discuss. Be comfortable with silence. And comfort families, regardless of the decision.
In the Southwest, Darryl Madalena encourages tribal members to think about becoming organ donors by making a connection between kidney disease — which afflicts Native Americans at higher rates than the U.S. population — and organ donation and receipt.
He talks about tribes’ increasing reliance on Western medicine and asks, hypothetically, if members would be prevented from journeying on if they had a pacemaker or an artificial hip. If not, why not donate or receive an organ?
“So much of westernized medicine is in the fabric of our communities, our lives, our culture,” said Madalena, the Native American liaison for New Mexico Donor Services. “If you pull one string, that may be very detrimental to the health of Natives.”
Madalena’s work is partly driven by the memory of his partner, Mylia Phouamkha, a Hopi woman who died within a week of being hospitalized with liver problems in 2019, without enough time to seriously consider a transplant.
She and Madalena had a son together, Micca, who was 2 years old at the time.
“If your heart tells you and you have it within yourself to have a transplant if you need it ...I would say yes, do it,” said her father, Myron Ami, as Micca sat on his lap.
Madalena has faced criticism for mentioning death, which can be a taboo topic. His community of Jemez Pueblo in New Mexico believes that people enter this world physically and spiritually whole, and that they should leave the same way.
“That’s what we’re taught, that’s what the beliefs still are,” he said.
The Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians doesn’t hold the same beliefs, Joan Azure said. About 40% of people in Rollette County where the tribe is based have signed up to become organ donors, compared to 65% overall in North Dakota.
Education, means or opportunity are big factors, said Mau Larson. Simply getting a driver’s license means traveling 80 miles (130 kilometers) from the Turtle Mountain reservation. But tribal IDs are renewed every two years, giving tribal members a more frequent opportunity to choose organ donation.
Studies show that organ recipients are best matched with donors of similar genetic makeup, Mau Larson said. Kidneys are especially needed in Native American communities, where one-quarter of the population is diabetic, she said.
Greyson and his family spent much of his life in Rochester, Minnesota, for his medical care, hundreds of miles from the rolling hills and lakes of the Turtle Mountain reservation. His heart came from a girl named Coralynn, whose picture on a puzzle piece was interlocked with Greyson’s on a parade float banner reading “Not all Heroes Wear Capes!”
After Greyson died, his family asked a Turtle Mountain elder to to bestow a traditional name upon him, through their creator. The elder was in a sweat lodge praying when it came to him: “Waasizo Gichi Anong Ningaabii' Anong,” or “Shining Big Star in the West," said Joan Azure.
“Even in his worst moments, his smile shined brightly, his presence brought happiness and light to everyone he came into contact with," she said. “And he provided guidance to many with that bright shining light through his bravery and strength.”
___
Fonseca reported from Flagstaff, Arizona. Fonseca covers Indigenous communities on the AP's Race and Ethnicity Team. Follow her on Twitter: @FonsecaAP. Contributing to this report were Associated Press writers Susan Montoya Bryan in Albuquerque, New Mexico, and Dave Kolpack in Belcourt, North Dakota.
Felicia Fonseca, The Associated Press